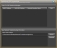
Troubleshoot HAL Connectivity
- In the Applicationsection on the Halogen toolbar, click the drop-down arrow in next to the Help button, then select Troubleshoot HAL Connectivity:
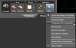
You can also open the Troubleshoot HAL Connectivity window from the Connect to Device and the Apply Configuration to Device dialogs. Both of these windows in include a Troubleshoot button in the lower right corner, which opens the dialog:

Sometimes, despite our best efforts to make connecting to a HAL as easy as possible, the Connect or Apply window doesn’t include a HAL that you know should be there. Since there are many network settings and software applications that are outside the control of Halogen and Ranelink, we have included a troubleshooter to help find out what’s interfering with Halogen’s ability to detect and connect to a HAL.
If your Connect or Apply Window is empty and it shouldn’t be, open the Troubleshoot HAL Connectivity window and click the Start button. When you do this, Halogen starts listening for the messages that all HALs periodically broadcast on the network. When Halogen receives one of these messages, it displays it in the window on the left. If no messages are displayed, then something is stopping them before they get to Halogen. That something might be a firewall or other security software, a bad cable, a defective network adapter, or a problem with your HAL. Press the Stop button or close the window to stop listening.
For really in-depth troubleshooting, the bottom half of the dialog allows you to run a series of diagnostic commands and save the results to a file for RANE technical support to analyze. As it executes each command Halogen updates the status in the lower left so you can see the progress. The diagnostics include:
- IP Configuration – the information saved is the same as if you were to type “ipconfig /all” at the command line.
- ARP Settings – the information saved is the same as if you were to type “arp -a” at the command line.
- Route Settings – the information saved is the same as if you were to type “route print” at the command line.
- Firewall Settings – this retrieves information about the Windows Firewall, including the rules related to exceptions needed for Halogen to communicate with a HAL.
- Broadcast Messages – Halogen listens for HAL broadcast messages for 30 seconds on each of the network interfaces and saves the results.
- HAL Pings – Halogen tries to ping each of the HALs identified by the broadcast messages and saves the results.
- Is RaneLink Running? – Check to see if the RaneLink service is running.
- RaneLink Log File – the RaneLink logfile is saved.
- Event Log – Windows Application Event Log entries written by RaneLink are saved, along with information about the event log itself (the size of the event log and whether it is set to overwrite old events.)
- Pipe Checks – A list of the open named pipes is saved. (Halogen communicates with RaneLink over named pipes.)
- OS and Security Information – Some basic information about Windows, such as version, 32 vs. 64bit, CPU speed, is saved. In addition, a list of installed Firewalls, Antivirus Products and Antispyware products is saved.
Details of the user interface elements are as follows:
| UI Element | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Start/Stop Button | Start listening for HAL broadcast messages on all available network interfaces. When you press Start, the button changes to Stop. |
| Listen for HAL Broadcast Messages area |
Displays the HAL broadcast messages as they are received. The HAL IP Address and HAL MAC Address identify the HAL that is sending the message and the Network Interface Name identifies which network connection on the PC is receiving the message. (On PCs with multiple NICs, such as a laptop with a wired connection and a WIFI network, it is important to know which connection is being used when troubleshooting connectivity issues.) |
| Browse | Allows you to select the file that will be created when the diagnostic routine runs. |
| Generate | This starts the diagnostic routine. As it runs, watch the status area for progress. |
| Name and Location | Displays the name of the file that Halogen creates when you hit the Generate button |
| Status area | Displays each step of the diagnostic routine as it runs. |
 See Also
See Also- Application Settings
- Apply Configuration to Device Dialog Box
- Birds-eye View Navigation Tool
- Common Features in Halogen Dialog Boxes
- Configuration Notes
- Configuration Settings
- Connect to Device
- HAL Model Picker
- Halogen Application Toolbar
- Halogen Startup Panel
- Hardware Map Display Controls
- Processing Map Display Controls
- Resolving Device Mismatch, Missing or Unexpected
- Restarting the RaneLink II Service
- Starter Configurations
- The Overall Halogen Framework
- Troubleshooting DR Devices
- Troubleshooting EXP Devices
- Troubleshooting RAD Devices
- Troubleshooting Resource Usage
- Troubleshooting the HAL Connection
- Troubleshooting the HAL Hardware
- Using Meters to Troubleshoot
- Viewing Current Error and Warning States
- Working with DHCP, DNS, Static IP Addresses, and Gateways